Airless technique of paint sprayers
Dec 21, 2022
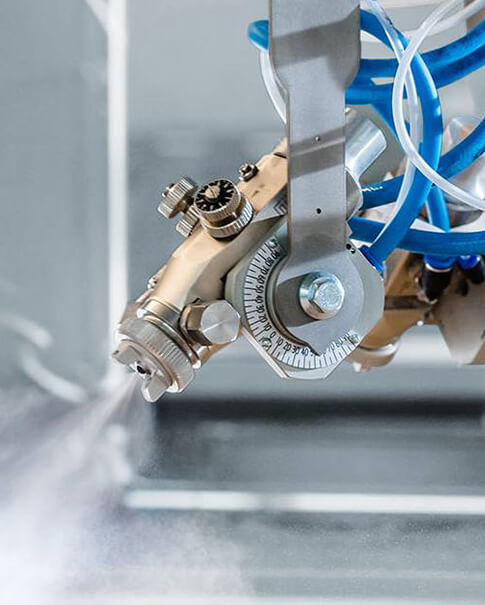
Various techniques are used in paint spraying. One of the best known techniques is the "airless" technique. Airless literally means 'without air' and, as many people believe, it produces little or no overs pray. In fact, the paint is forced under pressure through a small hole in the nozzle, so mark x airless paint sprayer are not actually 'airless'.
An airless sprayer usually consists of a suction pump which forces the paint under pressure through the nozzle. The paint can be emulsions, stains, wall coatings, primers and undercoats or any other water-based and/or synthetic-based liquid. Structural paints (granular solids) cannot normally be sprayed by airless machines.
Almost all types of paint can be applied using airless spraying. This is because it is available in hundreds of special nozzle sizes, from those that can handle very viscous liquids to those that can handle very thin liquids. Simply snap the nozzle into the paint gun and you can easily change to thicker or thinner paints.
Airless sprayers are usually better suited to spraying large areas and in almost all cases are a practical solution for interior wall paints (emulsions). Almost any airless sprayer can handle large painting and staining projects. If you want to spray thicker paint for outdoor projects (outdoor latex), specialist paints or fire retardants, you will usually need a larger nozzle. You should double check that the machine you buy has sufficient capacity for the job. The instruction manual that comes with each paint sprayer will explain the maximum tip size that the machine can accommodate.
Airless spray tips represent spray results, large surface areas, durability, spray patterns and relatively long cleaning and set-up times. Due to the relatively wide spray pattern (over spray), you will need more tape than with other techniques. However, once you start, you will soon be creating very good finishes on walls, blinds, woodwork, boats etc.
Commonly used projects with airless sprayers are: interior and exterior walls, wooden (garden) sheds, boats (especially with two-component coatings), series furniture, doors, floors, impregnation work, etc.